VIKAS (an acronym for Vikram Ambalal
Sarabhai) is a family of liquid-fuelled rocket engines conceptualized
and designed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre since the 1970s.
The early production VIKAS engines used imported French components which
were later replaced by domestically produced equivalents. It is used in
the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite
Launch Vehicle (GSLV) series of expendable launch vehicles for space launch
use. VIKAS engines are used to power the second stage PSLV, boosters and
second stage of GSLV Mark I and II and now the first stage of GSLV Mark
III (LVM3).Update 28.07.2022
Two new types of Vikas engines, HTVE (High Thrust
VIKAS Engine) and HPVE (High Pressure
or Highspeed VIKAS
Engine), are of particular interest,
but there are only confusing reports and photos.
"The next generation Vikas engine developed by the Liquid
Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) is being flown for the first time. LPSC
director Narayanan told that the improved engine would give a significant
advantage in terms of enhancing payload capability. Usually, the chamber
pressure is 58 bar, but with the use of high-thrust Vikas engine, we will
achieve 62 bar, which is a 6% increase in thrust that gives us 70 kgs
of additional payload gain. Right now, we are going to use the high-thrust
Vikas engine only in the second stage. Basically, we are validating it.
For Chandrayaan-2 mission, we will be using five such engines aiming for
a payload gain of around 250 kgs�.
It seems that:
-
The HTVE are modified VIKAS-2B engines and should
primarily be used for the second stage of the GSLV. For three LVM3 launcher
(X, D1 and D2), a SL-version of it was used of it.
-
The HPVE (= HsVE)
is a significantly modified VIKAS engines. Two different versions are
being developed for the GSLV booster and the first stage of the future
LVM3 (M).
-
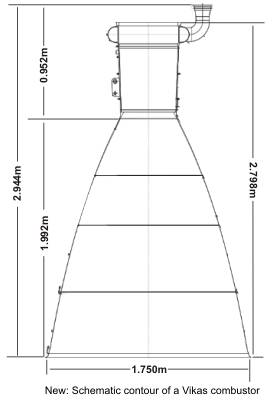
The development of the HPVE has been going on
since at least 10 years. There are pictures of the combustors in the
test or mounted on LVM3 demonstrators.
-
The first qualification-test of the reworked combustor
for the LVM3 (M) was occurred on January 20, 2022 (25 sec). Three more
long duration tests are planned.
|
|