|
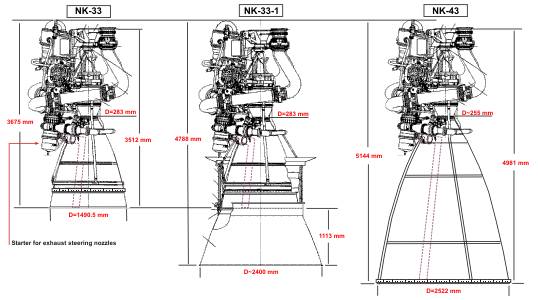
Variants of the Soviet rocket engine Kuznetsov
NK
(parameters and images)
The NK engines are the first Russian engines with a closed cycle. The second
generation of these engines (NK-33, NK-43), intended for the N-1F, have been
improved. They are also thrust adjustable and re-ignitable. This eliminates
the gradual shutdown of engine groups as in the first generation for the N-1.
The working gas for the turbine is generated in the gas generator (better
preburner) by burning with excess oxygen. The performance of the turbine and
thus of the engine can be changed by varying the excess oxygen in the gas
generator. In this way, a thrust between 100 and 50% of the nominal thrust
can be achieved. However, this only applies to the second generation of these
engines, which were intended for the N-1F.
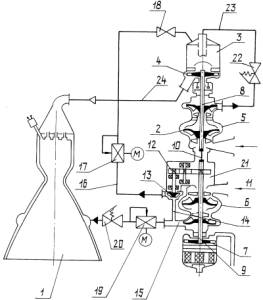
All NK engines are potentially equipped with yaw, pitch and roll controls.
Such regulations are carried out with exhaust nozzles via digital commands.
For this purpose, part of the working gas is used after passing through the
turbine by feeding it into nozzles. However, only selected engines are actively
used for this, two or more (?) for each steering nozzle.
The part of the working gas that is branched off is fed into a small, separate
pot with an exhaust pipe. From this pot, the control nozzles are supplied
via valves by command. This pot includes an on and off mechanism. When the
steerins are is finished, the valves are closed and the supplied exhaust gas
escapes unused through the pipe. However, re-operation is possible. With engines
that are not used for the control, an exhaust gas supply to the pot is permanently
prevented.
Most of the working gas from the preburner is fed into the combustion chamber
together with the fuel and serves to increase the pressure.
In July 1970, Kuznetsov received an order to develop significantly improved
engines for the first and second stages of the N-1. However, it was to take
another three years before these engines, designated NK-33 and NK-43, were
available. They could at first time be used for the N-1F.
Finally five improved NK engines was developed by Kuznetsov:
The new NK-33 and NK-43 engines for the N-1F (upgraded versions of the NK-15
and NK-15V). The NK-31 and NK-39 engines (upgraded versions of the NK-21 and
NK-19) and already available for the N-1 (6L and 7L). Two of the N-1F launcher
(8L and 9L) had been fully assembled and readied on pad for flight. But in
1974 the program was cancelled. The two N-1F launcher were scrapped, the engines
had previously been removed.
NK-9 type
|
Engine
|
NK-9
|
NK-9V
|
NK-19
|
NK-21
|
NK-31
|
NK-35 (LH2/LOX)
|
NK-39
|
NK-39K
|
|
Index
|
8D517
|
8D517V
|
11D53
|
11D59
|
11D 114
|
?
|
11D113
|
?
|
|
Use
|
GR-1 ICBM |
GR-1 / N-1 |
N-1 |
N-1 |
N-1 / N-1F |
UR-700 |
N-1 / N-1F |
Spaceplane |
|
Stage
|
1 |
2
/ 3,4, 5 (W,G,D) |
3
(W) |
4
(G) |
4
(G) |
? |
3
(W) |
1 |
|
Thrust s.l. (t)
|
38 |
-
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
29.8 |
|
Thrust vac (t)
|
43.5 |
46
|
46 |
41
|
41 |
200 |
41.5 |
37.7 |
|
Isp s.l. (sec)
|
286.5
|
-
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
255.1 |
|
Isp vac (sec)
|
328
|
345
|
345 |
340 |
353 |
? |
352 |
322.7 |
|
Chamber pressure
|
? |
10.34
MPa (?) |
? |
? |
9.20
MPa |
? |
9.20
MPa |
9.20
MPa |
|
Nozzle area ratio
|
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
114 |
? |
|
Flow rate (kg/sec)
|
132.6
|
133.3
|
133.3 |
120.1 |
116.1 |
|
117.9 |
116.8
|
|
O/F mix
|
2.50 |
2.50 |
2.50 |
2.50 |
2.60 |
|
2.60 |
2.60
|
|
Image
|
?
|

|
?
|
 |

|
 |

|

|
| |
|
similar
NK-9V |
|
|
not
realized |
|
here
without nozzle |
NK-15 type
|
Engine
|
NK-15
|
NK-15V
|
NK-33
|
NK-33-1
|
NK-33M
|
NK-33MN |
NK-43
|
NK-43M
|
|
Index
|
11D51
|
11D52
|
11D111
|
|
|
|
11D112
|
|
|
Use
|
N-1 |
N-1 |
N-1F, Soyuz-1 |
Soyuz |
Yamal |
Polyot Air launch |
N-1F |
Polyot Air launch |
|
Stage
|
1 (A) |
2 (B) |
1 (A) |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 (B) |
1 |
|
Thrust s.l. (t)
|
140.6
|
-
|
154 |
185 |
~169.2 |
~176.7 |
- |
- |
|
Thrust vac (t)
|
157.4
|
168
|
171.5 |
202.6 |
188 |
196 |
179.2 |
212 |
|
Isp s.l. (sec)
|
284
|
-
|
297.2 |
304.9 |
~306 |
~311 |
- |
- |
|
Isp vac (sec)
|
318
|
325
|
331 |
333.9 |
~340 |
~345 |
346 |
349 |
|
Chamber pressure
|
?
|
?
|
14.53
MPa |
17.16 MPa
|
? |
? |
14.57
MPa |
17.16 MPa
|
|
Nozzle area ratio
|
|
|
27.7 |
~71.9 |
|
|
79.7 |
79.7 |
|
Flow rate (kg/sec)
|
495.0
|
516.9
|
517.9
|
606.8
|
|
|
517.9 |
607.4
|
|
O/F mix
|
2.50
|
2.50
|
2.60
|
2.60 |
2.60
|
2.60 |
2.80 |
2.80 |
|
Image
|

|

|
 |
 |
? |
? |
 |
? |
|
source: alabin.ru |
source: alabin.ru |
restartable |
modified NK-33 |
similar NK-33 |
similar NK-33 |
restartable |
similar NK-43 |
Derivative
|
Engine
|
AJ-26-58
|
AJ-26-59 |
AJ-26-60
|
AJ-26-62
|

|
|
Index
|
(NK-33)
|
(NK-33) |
(NK-43)
|
(NK-33)
|
|
Use
|
Kistler K-1 |
Kistler K-1 |
Kistler K-1 |
Antares |
|
Stage
|
1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
Thrust s.l. (t)
|
154.2 |
154.2 |
- |
154.2
/ 166.5 |
|
Thrust vac (t)
|
171.9 |
171.9 |
180.4 |
171.4
/ 185.1 |
|
Isp s.l. (sec)
|
297.2 |
297.2 |
- |
300.4 |
|
Isp vac (sec)
|
331.3 |
331.3 |
348.3 |
334 |
|
Chamber pressure
|
14.54
MPa |
14.54
MPa |
14.57
MPa |
14.54
/ 15.70 MPa |
|
Nozzle area ratio
|
27.7 |
27.7 |
79.7 |
27.7 |
|
Flow rate (kg/sec)
|
518.8 |
518.8 |
517.9 |
513.2
/554.2 |
|
O/F mix
|
2.60 |
2.60 |
2.80 |
2.60 |
|
Image
|
 |
? |
 |
 |
similar NK-33
restartable |
similar AJ-26-58
restartable |
similar NK-43
restartable |
modified NK-33
throttle to 108% thrust |
|
|
Exhaust steering nozzles of block-W
|
|













